Recent Literature
Our Latest Reviews
TB006 (TrueBinding): An Inflammation-First Monoclonal Antibody Strategy for Alzheimers Disease
TB006 is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody developed by TrueBinding, Inc. to treat Alzheimer's disease. Unlike traditional approaches, TB006 neutralizes galectin-3, a lectin increasingly associated with disease progression, rather than targeting fibrillar amyloid directly.
Read moreNeflamapimod (VX-745): A Synaptic-Rescue Strategy in Neurodegenerative Disease
Neflamapimod (VX-745) is an oral small-molecule inhibitor of p38alpha MAP kinase, developed by CervoMed Inc. It targets neurodegenerative disorders marked by synaptic dysfunction and neuroinflammation, distinguishing itself from amyloid- or tau-directed approaches.
Read moreLiquid States of Failure: Phase Transitions as the Hidden Architecture of Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies
The classical model of protein aggregation from monomer to oligomer to fibril inadequately explains the structural and kinetic changes in tauopathies, synucleinopathies, ALS/FTD-spectrum disorders, and Huntington's disease. These neurodegenerative conditions display intrinsic complexity.
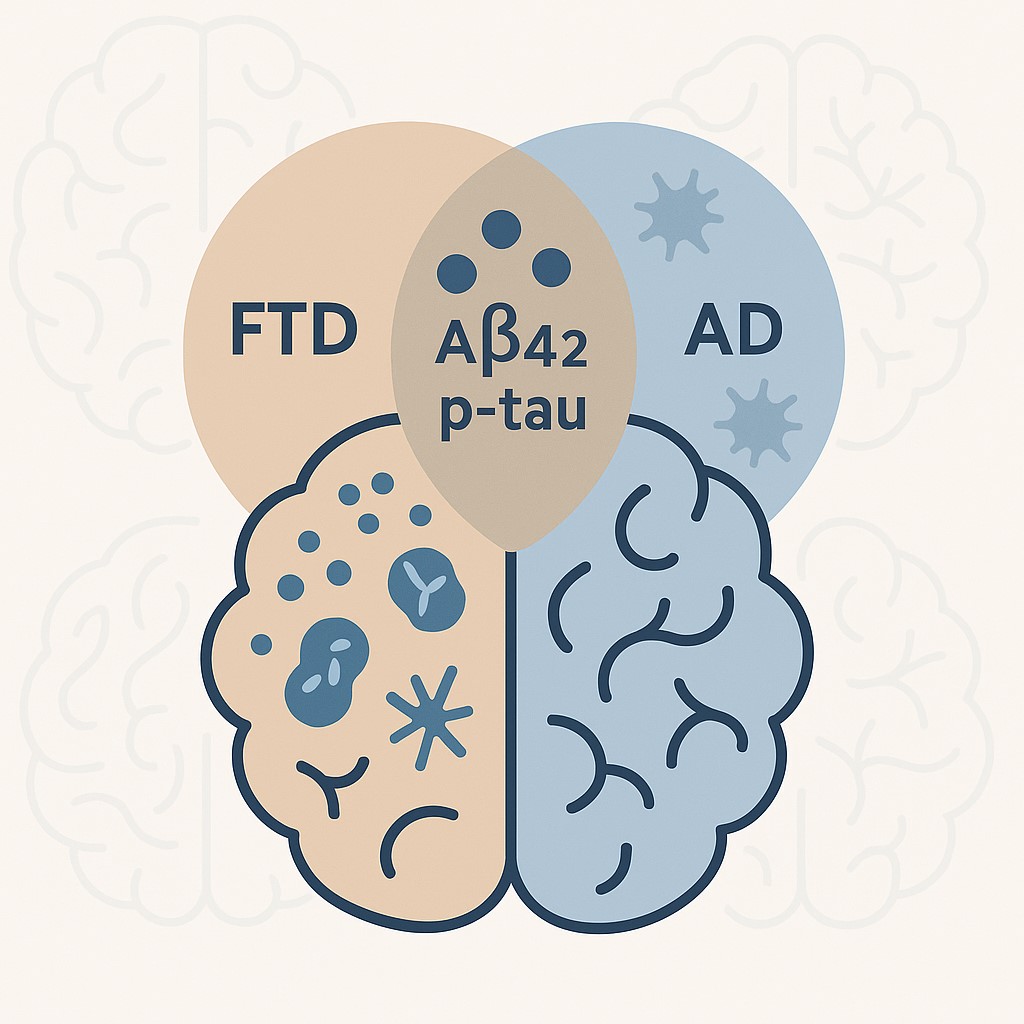
Read moreThe Diagnostic and Clinical Relevance of CSF Biomarkers in Alzheimers and Non-Alzheimer Dementias
A landmark study in JAMA Neurology* examined CSF biomarkers in 13,800 dementia patients, revealing AD-like profiles in both AD and non-AD cases. Biomarker findings suggest co-pathology in non-AD dementias, crucial for therapy selection. Integration of biomarkers into diagnoses must consider clinical context for personalized treatment.
Read morePrasinezumab: A Targeted alpha-Synuclein Antibody for Parkinson's Disease
Prasinezumab is an investigational monoclonal antibody targeting aggregated -synuclein in Parkinson's disease (PD). It aims to reduce neuronal toxicity and slow disease progression. Trials show it crosses the blood-brain barrier and may slow motor symptom progression, especially in rapidly advancing PD, though primary endpoints were unmet. It's generally well-tolerated, and ongoing studies aim to further assess its efficacy.
Read moreCerebellar Cognitive Impairment in Cerebellar Disorders
The study identifies two subtypes of Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome in cerebellar disorders using the German CCAS-Scale: severe and mild impairments. Findings highlight distinct cognitive deficits for tailored interventions. Limitations involve diagnostic sensitivity and patient heterogeneity, suggesting future research on refined tools and neuroimaging.
Read moreAlzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), now 20 years old, is a key player in Alzheimer's research, enhancing biomarker validation, clinical trials, and data sharing. It has driven over 6,000 publications and supported new treatments. Despite challenges like diversity and data complexity, ADNI4 aims to improve inclusivity and leverage AI. ADNI's open-access model and technological advancements continue to inspire similar initiatives globally.
Read moreCurrent and Novel Therapeutic Agents for Alzheimer\'s Disease: A Critical Appraisal
Alzheimer's disease is a global challenge, projected to affect 153 million by 2050. Current treatments are symptomatic, while new monoclonal antibodies offer limited benefits with risks. Promising therapies like ladostigil target inflammation and stress, emphasizing early intervention and multi-mechanistic strategies.
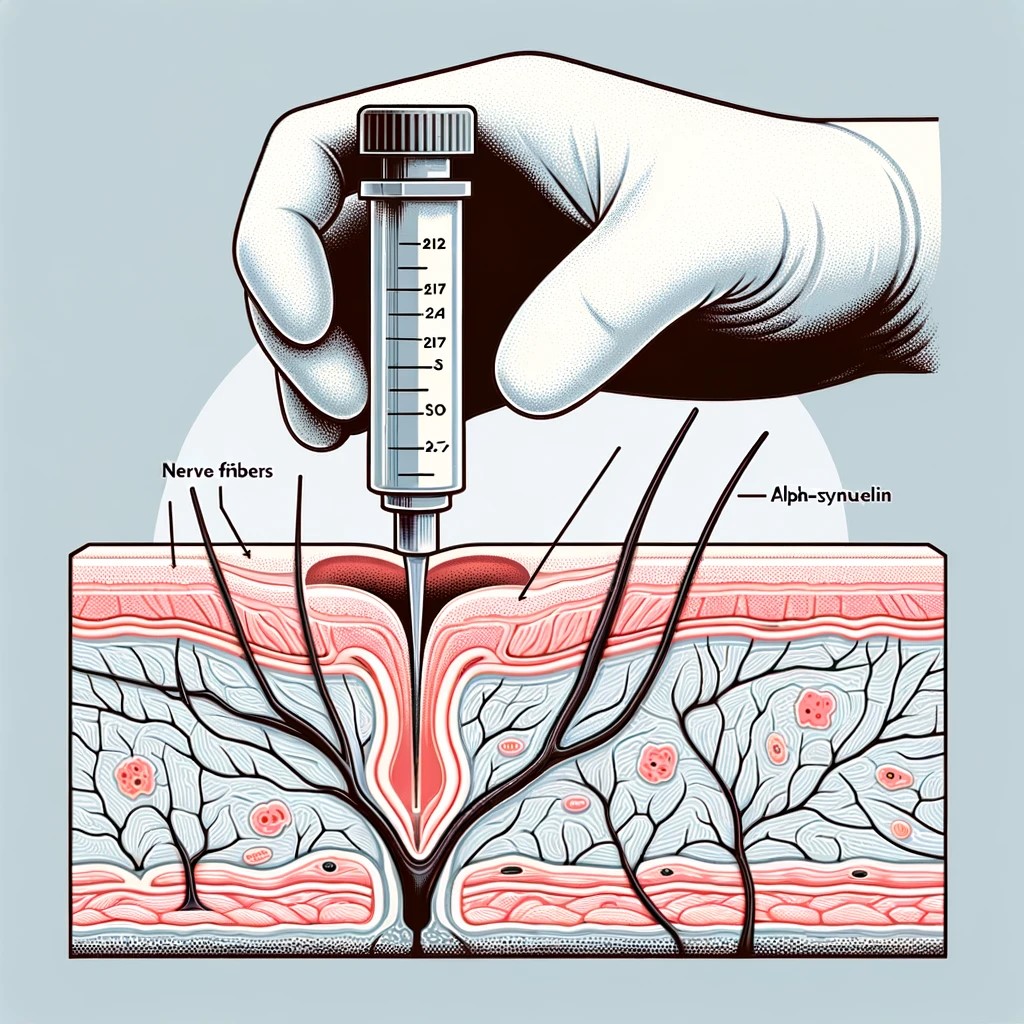
Read moreSkin Alpha-Synuclein as a Biomarker for Synucleinopathies
Skin alpha-synuclein detection is emerging as a promising biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, multiple system atrophy, and pure autonomic failure. This minimally invasive method shows high diagnostic sensitivity and can distinguish between these disorders.
Read moreAn Update on Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) is a rare, fatal neurodegenerative disorder marked by -synuclein buildup, causing parkinsonism, cerebellar symptoms, and autonomic dysfunction. Diagnosis is challenging, but updated criteria and biomarker research aim to improve early detection.
Read morePhotoBioModulation for Alzheimer's Disease
Photobiomodulation (PBM) uses red or near-infrared light to boost cellular activity and mitochondrial function, potentially benefiting Alzheimer's disease by reducing beta-amyloid plaques and improving cognition. Although preclinical studies are promising, more extensive human trials are needed to confirm its efficacy.
Read moreNilotinib for Parkinson's Disease
Nilotinib, a leukemia drug, initially showed promise for Parkinson's by inhibiting c-Abl protein and affected cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. However, larger trials showed no symptomatic improvement and poor brain penetration, necessitating further research on its biomarker effects and alternative strategies.
Read moreCentral Nervous System Involvement in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
This review explores CNS complications in adults with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, such as SLE and vasculitis. It emphasizes the need for individualized, syndrome-specific diagnostic and treatment plans, utilizing advanced tools and immunosuppressive therapies to manage complex manifestations.
Read moreExpanded Guide for Diagnosing Leukoencephalopathies Using MRI and Clinical Data
Diagnosing leukoencephalopathies involves MRI pattern analysis, distinguishing hypomyelination, and using genetic, clinical, and biochemical tests. This structured approach narrows down diagnoses, considers clinical correlation, and excludes acquired mimics to identify specific leukoencephalopathies.
Read moreExpanded Step-by-Step Summary for Analyzing MRIs in Suspected Leukoencephalopathies
Diagnosing leukoencephalopathies via MRI involves: confirming symmetric white matter involvement, differentiating hypomyelination/demyelination, assessing white matter patterns, correlating with clinical presentation, considering extra-neurological signs, and using ancillary tests like genetic analyses.
Read moreThe Potential of Music Therapy to Improve Cognitive and Emotional Health in Alzheimer's Disease
Music therapy is a promising non-drug treatment for Alzheimer's, aiding in symptom relief, mood, and cognitive and social functions. It may boost neuroplasticity and reduce inflammation. The ALMUTH study explores these effects, but further research is necessary.
Read moreExploring the Potential for Transfusion-Transmissible Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) involves beta-amyloid deposit in brain vessels, raising risks of hemorrhage and cognitive decline. While often sporadic and age-related, iatrogenic cases suggest potential transmissibility. A study hints at CAA's possible spread via blood transfusions, prompting further research into diagnostic methods and donor screening to address public health concerns.
Read moreUnderstanding the Interconnected Pathways between the Brain and Heart Health
The American Heart Association highlights the connection between cardiovascular health and cognitive function, noting that heart conditions can lead to cognitive decline. Early management and lifestyle interventions can reduce stroke risk and delay cognitive impairment, emphasizing prevention for brain health.
Read moreExploring Suvorexant's Potential in Alzheimer's Prevention
This study examines suvorexant's effects on Alzheimer's biomarkers, showing it reduces tau phosphorylation at T181 and lowers A levels in humans. It suggests suvorexant might act through orexin signaling pathways, indicating its potential as an AD prevention drug. Further research is needed to assess long-term impacts.
Read moreAD Biomarkers in DBS Screening
While biomarkers like a-synuclein are promising for PD, their use in AD for DBS is unexplored. Blood-based AD biomarkers show potential but need standardization and further research for DBS decision-making.
Read moreAHEAD 3-45 Study: Amyloid-Targeting in Alzheimer's Prevention
The AHEAD 3-45 Study investigates early intervention with lecanemab to slow Alzheimer's progression during its preclinical phase. It includes two trials, A3 and A45, targeting cognitively unimpaired individuals with varying amyloid levels. Innovative recruitment using biomarkers aims to improve efficiency. Lecanemab targets aggregated amyloid beta, potentially preventing Alzheimer's. The study's comprehensive design could shift Alzheimer's management by emphasizing early intervention.
Read moreDeprescribing Antihypertensives in Nursing Home Residents with Dementia
The study examines the impact of deprescribing antihypertensive medications on cognitive function in nursing home residents aged 65 and older. Results indicate that deprescribing is linked to a reduced risk of cognitive decline, especially in residents with dementia. The study highlights the need for individualized deprescribing approaches and further research to confirm benefits and address potential harms. It suggests deprescribing as a strategy to mitigate cognitive decline while emphasizing personalized treatment plans.
Read moreMild Closed-Head Impact Injuries and Early Onset of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
A study explored the link between mild closed-head impacts and chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) using human and animal models. It found early CTE signs, like astrocytosis and tau protein buildup, can arise from such injuries. The study highlights the need for more research on CTE's long-term effects and treatments.
Read moreA Global Call to Action on Modifiable Risk Factors and Holistic Care
The Lancet Commission's 2020 report highlights the rising prevalence of dementia. It identifies 12 modifiable risk factors, including alcohol, TBI, and air pollution, that could prevent 40% of cases. The report emphasizes lifelong prevention strategies, improved care, and the importance of addressing health disparities, especially in LMICs.
Read moreIdentifying Autoimmune Encephalitis in Older Adults
Autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) can mimic dementia syndromes, particularly in patients aged 45 or older. This study found that 38% of AIE cases resembled dementia, often with rapid cognitive decline. Key indicators for AIE include subtle seizures and atypical test results. Most patients improved with immunotherapy, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis.
Read morePredicting Dementia Survival
The study by Haaksma et al. developed a tool to estimate three-year survival probabilities in dementia patients using Swedish data. Key factors include age, sex, comorbidities, and dementia subtype. The tool aids care planning with prediction tables and a color-coded format, with a concordance index of 0.70 to 0.72. Validation in other countries is suggested.
Read moreComprehensive Management of Lewy Body Dementia
Taylor et al.'s review in *Lancet Neurology* discusses the challenges of managing Lewy body dementia (LBD), highlighting its diverse symptoms and fragmented care. Current treatments have limited efficacy. An interdisciplinary approach is recommended, and more research and global collaboration are needed to improve care.
Read moreThe role of alpha-synuclein phosphorylation in the healthy brain
The article challenges the traditional view of -synuclein phosphorylation at serine-129 (Ser129P) as a pathological marker, showing it regulates synaptic function by affecting neurotransmitter release and vesicle dynamics. Ser129P maintains synaptic homeostasis and could be a therapeutic target in synucleinopathies.
Read moreRevised Diagnostic and Staging Criteria for Alzheimers Disease
The Alzheimer's Association's updated criteria focus on biological markers such as amyloid-beta plaques and tau tangles for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. It integrates these with new blood-based markers, using Core 1 biomarkers for diagnosis and Core 2 for staging, across four biological and six clinical stages.
Read moreBehavioral Frontotemporal Dementia (bvFTD)
The 2011 revised criteria for diagnosing behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD) aim to improve early and accurate diagnosis. Developed by the International bvFTD Criteria Consortium, they outline possible, probable, and definite bvFTD, focusing on behavioral patterns, functional decline, and neuroimaging.
Read moreNew Genetic Discovery May Help Protect Against Alzheimer's in High-Risk Individuals
A study in Acta Neuropathologica found that rare genetic variations in the FN1 gene may protect APOE4 carriers from Alzheimer's. The FN1 variant rs140926439 reduced risk and delayed onset. Zebrafish models showed improved responses, suggesting that targeting ECM processes could be therapeutic.
Read moreRepurposing IDO1 Inhibitors to Restore Cognitive Function in Alzheimer's Disease
The study by Minhas et al. proposes targeting astrocytic metabolism via IDO1 inhibition as an Alzheimer's therapy, shifting focus from amyloid-beta and tau to glial metabolism. It shows promise in restoring glucose metabolism and memory, but relies on animal models and lacks long-term human effects. It opens new avenues for metabolic interventions in AD.
Read moreAre Heartburn Medications Safe Long-Term? Exploring the Hidden Risks of Proton Pump Inhibitors
The article explores long-term proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use, noting risks like nutrient deficiencies, renal disease, infections, dementia, and cardiovascular issues. It emphasizes the need for further research and advises evaluating PPI necessity carefully, especially for high-risk groups, using the lowest effective dose.
Read moreHow Specially Designed Music Can Boost Focus for People with ADHD
The study shows that amplitude-modulated music can enhance cognitive performance, particularly sustained attention, by interacting with brain oscillations. Participants with higher attentional difficulties benefited most, suggesting music as a non-invasive, low-risk way to improve attention.
Read morePsychedelic Therapy May Boost Well-Being and Social Connection in Depression Treatment
A 6-month follow-up of a phase 2 trial comparing psilocybin therapy and escitalopram for major depressive disorder showed both improved depression, with psilocybin offering greater benefits in social functioning and life meaning. No significant safety differences were noted.
Read moreNew Curcumin-Based Compounds Show Promise in Fighting Alzheimer's-Linked Brain Protein Tangles
The article discusses novel curcumin derivatives as a therapeutic strategy to reduce toxic tau oligomers in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, highlighting their ability to decrease tau toxicity and promote non-toxic aggregate formation.
Read moreHigh-Dose Vitamin B12 Shows Promise in Slowing Early ALS Progression
The trial shows ultrahigh-dose methylcobalamin may slow ALS progression, offering clinical benefits with minimal side effects, especially in early stages. Early intervention is crucial, and combining methylcobalamin with therapies like riluzole could improve outcomes.
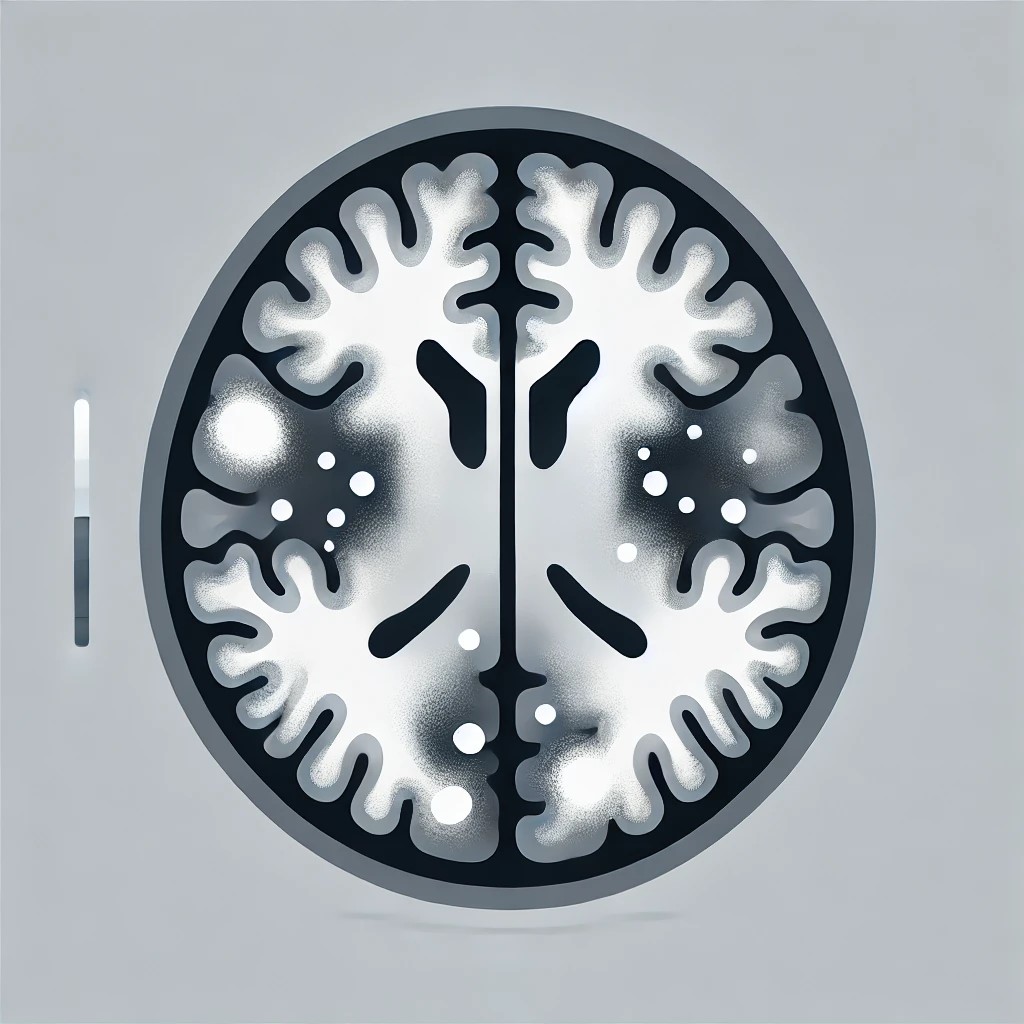
Read moreNew Brain Scan Technique Helps Predict Alzheimer's Progression in Early Stages
The study of 448 participants found tau PET to be the most accurate standalone predictor for MCI progression to dementia, outperforming A PET and MRI. Tau PET combined with MRI gave the best risk prediction, especially in younger individuals and APOE4 non-carriers, highlighting tau PET's promise as a prognostic marker.
Read moreHow Collagen Protects the Aging Brain
The study highlights collagen VI's vital role in safeguarding the central nervous system against neurodegeneration in aging. A collagen VI null mouse model showed that its deficiency causes increased neuronal apoptosis, disrupted autophagy, and oxidative stress.
Read moreUnderstanding Collagen VI: A Key Protein in Nerve Health and Brain Disorders
This article offers a comprehensive review of collagen VIs emerging role...
Read moreA Biomarker-Centric Framework for Early Detection and Progression Monitoring
The Alzheimer's Association Workgroup's revised criteria emphasize a biological approach, focusing on neuropathologic changes for diagnosis. It introduces a four-stage model (Stages A-D) using biomarkers like amyloid PET for early detection. The criteria support clinical evaluations and highlight the need for diverse research cohorts.
Read moreThe article highlights synaptic oligomeric tau's crucial role in early Alzheimer's, suggesting its accumulation at synapses drives pathology and synapse loss. It reveals tau spreads trans-synaptically, presenting a novel therapeutic target to prevent Alzheimer's progression.
Read moreEzetimibe potential neuroprotective?
This article highlights a breakthrough in Alzheimer's research, showing that the cholesterol drug ezetimibe can reduce neurodegenerative protein aggregation. This discovery suggests new prevention strategies for Alzheimer's and other dementias, especially in high-risk groups, by repurposing existing medications.
Read moreThis study advances understanding of the X chromosome's role in Alzheimer's disease, identifying new risk loci and emphasizing the importance of sex differences in genetic research. It opens pathways for future research into X-linked genetic variations and their impact on Alzheimer's pathology.
Read moreThe review links pathogens such as HSV-1, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Porphyromonas gingivalis to Alzheimer's disease, suggesting they may enter the brain through a compromised blood-brain barrier or nerve pathways, causing chronic inflammation and accelerating AD pathology.
Read moreSaunas are neuroprotective?
The article provides compelling evidence that mild hyperthermia, whether induced by sauna-like conditions or menthol treatment, could reduce tau phosphorylation, offering promising new avenues for treating Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. These findings contribute to a growing body of research exploring non-pharmacological approaches to slowing neurodegenerative disease progression.
Read moreThis article provides significant insights into the pathological role of tau-RNA interactions in Alzheimer's disease and othertauopathies, revealing that RNA binding may be a critical factor in tau aggregation and neurodegeneration, suggesting new therapeutic targets to combat tau-related disorders.
Read moreImmunomodulatory properties of menthol in Alzheimer Disease
The article highlights the promising intersection of immunology, neuroscience, and olfaction, showing that immune system interventions like menthol inhalation or Treg depletion can significantly impact cognitive function in neurodegenerative diseases, paving the way for new Alzheimer's therapies.
Read more